CardioMender, MD recently conducted an internal study on new patients who had NO prior history of Type-2 Diabetes, Pre-diabetes, or insulin resistance. Our results were shocking!
The majority of patients had an abnormally high Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), a blood test used to identify Pre-Diabetes and Type-2 Diabetes.
The HbA1c is a simple blood test that does not require fasting when obtained. If above normal, it identifies the presence of insulin resistance which, if left unchecked, is a root cause of Type-2 Diabetes and many common life threatening, but potentially reversible, illnesses.

What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas whose primary function is to regulate blood sugar. Increasing belly fat leads to the occurrence of insulin resistance, an impairment of insulin function, in those susceptible to it. Initially, the pancreas produces more insulin in an attempt to control blood sugar. However, increasing insulin levels impairs our ability to burn fat and also leads to increased fat production. Thus, the situation snowballs. This puts extreme stress on the pancreas and over time causes the pancreas to “burn out” and fail. When extreme, pancreatic failure requires insulin therapy to control blood sugar, further impairing weight loss and the ability to maintain good health.
Simply put, being overweight can lead to insulin resistance, while weight loss plays a critical role in reversing insulin resistance.
The sooner insulin resistance is identified and the belly fat is reduced , the greater the likelihood of reversing its long term consequences, so reversing insulin resistance will help maintain pancreatic function, optimal health and vitality. It will also make weight loss easier to achieve and maintain. The following explains why it is important to prevent or reverse insulin resistance.
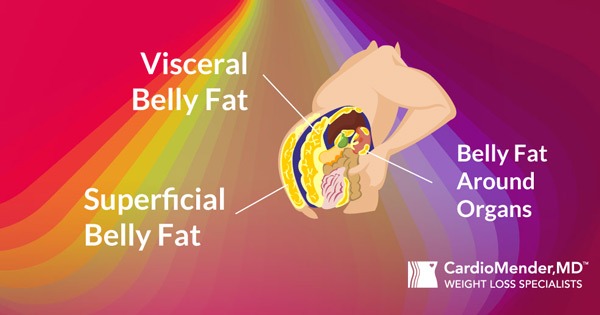
Common Conditions Associated with Insulin Resistance
Pre-Diabetes: If left unchecked, Pre-Diabetes leads to Type-2 Diabetes. Insulin resistance is initially associated with increased insulin levels, which stimulates fat production and impairs fat burning. Later, insulin resistance results in falling insulin production resulting in increased blood sugars.
Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus: This is extreme and inadequately compensated insulin resistance. It is associated with increased risk of stroke, heart attacks, kidney failure, pancreatic failure and infections, and is predated by insulin resistant pre-diabetes.
Abnormal Blood Fats: Insulin resistance is associated with reduction in HDL or “Good Cholesterol”, increase in pathologic LDL cholesterol or “Bad cholesterol” and increased Triglycerides which are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, pancreatitis and other medical conditions.
Hypertension: Insulin resistance is believed to frequently play a role in causing hypertension, or high blood pressure, which is associated with increased risk of stroke, heart attack and kidney disease. Half of primary hypertension, high blood pressure without an identifiable cause, is thought to be due to insulin resistance.1
Metabolic Syndrome: This is a condition comprised of a group of symptoms which increase the risk of, among other illnesses, cardiovascular disease, heart disease, stroke and Type-2 Diabetes.
How do you know if you have Metabolic Syndrome?
You have Metabolic Syndrome if you have at least three of the following measurements:
- Categorized as Abdominal obesity
- Men with waist circumference of 40 inches or more
- Women with waist circumference of 35 inches or more
- Fasting glucose greater than 100 mg/dL or HbA1c greater than 5.7
- Blood pressure above 135/85 mm Hg
- Triglycerides over 150 mg/dL
- Reduced HDL (good) cholesterol as follows:
- Men under 40 mg/dL
- Women under 50 mg/dL
PCOS (PolyCystic Ovary Syndrome):This most common endocrine disorder of pre-menopausal women2 is thought to be preceded by the development of insulin resistance.3 PCOS is associated with decreased fertility, irregular menses, increased testosterone, acne, increased body hair and the presence of ovarian cysts.
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Insulin resistance increases the risk of fatty infiltration of the liver which can lead to permanent liver damage, including cirrhosis.
Cancer: Insulin resistance is associated with colon and uterine cancer, and possibly pancreatic, renal and breast cancer.

The Challenge
Insulin resistance hinders the ability to burn belly fat and fat in general. Therefore, the challenge is to be able to lose weight, burn fat and better control blood sugar levels, all while the body itself is interfering with the capacity to do so. But it is possible!

The Solution
CardioMender, MD Weight Loss Specialists deals with cases of insulin resistance every day. All of our New Patient visits and Restart visits now include blood tests for an HbA1c and a comprehensive metabolic package. Have us identify your risks and help you safely achieve and maintain a healthy weight and optimal health!
Learn more about How to Lose Belly Fat in our three-part series. Click here.
Read about two of our solutions, CardioMetabolic Lean and Calcium Pyruvate
You’ve Got to Live It!TM
References:
1. Reaven GM., Insulin resistance/compensatory hyperinsulinemia, essential hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. J Clin, EndocrinolMetab. 2003;88:2399–403.
2. Reaven G., The metabolic syndrome or the insulin resistance syndrome? Different names, different concepts, and different goals. EndocrinolMetabClin North Am. 2004;33:283–303.
3. Wilcox, Gisela,Insulin and Insulin Resistance, ClinBiochem Rev. 2005 May; 26(2): 19–39. PMCID: PMC1204764
Melbourne Pathology, Collingwood, VIC 3066, Monash University Department of Medicine & Clinical Nutrition & Metabolism Unit, C/- Body Composition Laboratory, Monash Medical Centre, Clayton, VIC 3168, Australia






