We now move on to what we can do about this.

But first, you can review Part 1 about electrolyte deficiency here, if you like.
Replacement and Maintenance:
Magnesium supplementation may drastically lower rates of chronic symptoms related to insulin resistance, Cardiovascular disease, nervous system disorders including migraines, pain from muscle cramps, and tension.† In fact some researchers have concluded the following:
“It is our conviction that many patients with … attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) would have their symptoms improved through Magnesium therapy.”
Similarly, patients with the following diagnoses may have low magnesium [10] and may benefit from magnesium supplementation.
- Diabetes mellitus
- Cardiovascular disease (i.e. coronary artery disease, stroke, hypertension)
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Depression
- Migraine and cluster headaches
- Muscle cramps
- Abdominal pain
- Weakness
- Osteoporosis
- Asthma
- Stress disorders
- Tinnitus (ringing in ears)
- Confusion
- Preeclampsia
- Epilepsy
- Tremor
- Parkinsonism
- Neuro-vegetative disorders
Additionally, certain forms of insomnia have been improved with magnesium supplementation.
How can we get more magnesium?
Ideally we would get all we need from the foods we eat. Here is a partial list of dietary sources [11]:
- Dark leafy greens i.e. spinach, Swiss chard, kale, collard greens, seaweed agar
- Dried spices i.e. basil and coriander
- Seeds i.e. Brazil nuts, almonds, pumpkin and sesame seeds
- Fish (most varieties) i.e. Mackerel and Tuna
- Flaxseed
- Beans i.e. soy and lentils
- Whole grains
- Avocados
- Low fat dairy
- Dried fruit i.e. figs
- Cocoa, dried
For a more comprehensive list of foods and their nutrient content including magnesium, go to the Department of Agriculture’s (USDA’s) Nutrient Database Website here.
However, it is difficult to get all the magnesium we need in our diet, one reason being that over-farming has depleted many nutrients from our soils, in addition to the other reasons stated previously.
Supplements: If you are not able to get enough magnesium in your diet you may want to choose a supplement.
Magnesium supplements vary profoundly in their absorption, bioavailability and potential side effects. (See table below) It is also important to be aware that supplementation with other minerals i.e. calcium, phosphorous, iron, copper and manganese can compete with and reduce magnesium absorption.[12]
Table of Magnesium Supplements and properties [13]:
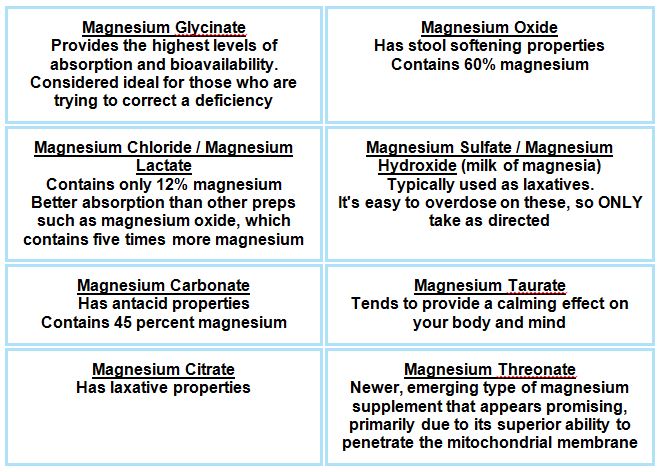
Risks from Magnesium Supplementation
There is virtually no risk to excess magnesium supplementation in people with normal kidney function. The likelihood of magnesium toxicity increases in people with impaired kidney function. Excessive magnesium supplementation can cause diarrhea and abdominal symptoms such as cramping and nausea.
Schedule an appointment with our weight loss and wellness physicians today or consult your healthcare provider to see if you are a candidate for magnesium supplementation and what supplement is appropriate for you.
CardioMender, MD Nutraceuticals is proud to offer our new pharmaceutical grade magnesium supplement:

Magnesium Glycinate
- Delivers fast and efficient absorption not found in many other magnesium preparations
- Excellent bioavailability to ensure your body gets the full benefit
- Pharmaceutical grade
- Quality Assurance Tested – Get what you pay for without impurities
- Safety
Learn more about CardioMender, MD’s Magnesium Glycinate here.
† These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
References:
[10] Dierck-Hartmut Liebscher, MD, Dr Sc Nat, Dierck-Ekkehard Liebscher, Dr Sc Nat Self-Help Organisation on Mineral Imbalances, Task Force Magnesium-Deficiency Tetany, Berlin, GERMANY Key words: Magnesium-deficiency tetany, self-help, diagnosis, serum analysis &
Journal of the American College of Nutrition by Doctors Dierck-Hartmut Liebscher, MD, and Dierck-Ekkehard Liebscher, MD. “About the Misdiagnosis of Magnesium Deficiency”
[11] Source- https://www.healthaliciousness.com/articles/foods-high-in-magnesium.php#magnesium-density-by-gram and Mercola.com
[12] http://www.ancient-minerals.com/magnesium-sources/absorption/
[13] http://articles.mercola.com/sites/articles/archive/2015/01/19/magnesium-deficiency.aspx



