Many people ask me what supplements I take in an effort to optimize my body’s natural immunity against COVID-19.  Obviously, there is no way to know with absolute certainty, but I have used the best available medical evidence, data and facts as the basis in my decision-making process. The following represents my initial conclusions on what supplements would help optimize my body’s immunity and be most likely to improve outcomes from exposure to the Coronavirus or COVID-19. This is my regimen of immune defense supplements and is by no means definitive or complete; I continue to study additional options.
Obviously, there is no way to know with absolute certainty, but I have used the best available medical evidence, data and facts as the basis in my decision-making process. The following represents my initial conclusions on what supplements would help optimize my body’s immunity and be most likely to improve outcomes from exposure to the Coronavirus or COVID-19. This is my regimen of immune defense supplements and is by no means definitive or complete; I continue to study additional options.
DOC’S IMMUNE DEFENSE SUPPORT PACKAGE
To Help Maintain Optimal Natural Immunity
- Vitamin D†
- Zinc
- Quercetin
- Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
- Melatonin
†CMMD recommends our patients check Vitamin D levels and recheck after 90 days of supplementation.
In my opinion, with the current knowledge available, these are the top five supplements most likely to optimize the maintenance of comprehensive immune support. That being said, until there’s a medical cure or a reliable vaccine, limiting potential exposure to the Coronavirus is the most effective protection against it, though for many, this may not be possible or practical. Complicating the situation, the evidence shows that 40 to 50% of COVID-19 infections are asymptomatic. Also, people who are asymptomatic or pre-symptomatic shed COVID-19 and can infect those they come in contact with.
Following is the backup to support my choices for my Immune Defense Regime:
Vitamin D
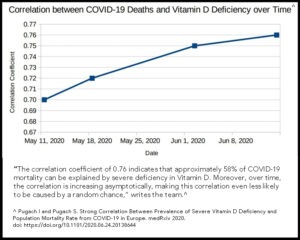
Medical studies suggest that low Vitamin D levels are an independent risk factor for getting COVID-19 infection and that extremely low Vitamin D levels are associated with more severe infections and worse outcomes.1,2,3,4 Some medical studies have shown that there is a decreased risk of upper respiratory tract infections with Vitamin D supplementation.5,6 That being said, it has not been proven that taking Vitamin D prevents or lessens the severity of COVID-19 infection.
Approximately 42% of adult Americans are Vitamin D deficient with the highest rates of deficiency found in blacks (82%) and Hispanics (69%).7 The fact that Vitamin D levels are generally lower in people of color may in part explain why COVID-19 seems to affect them more profoundly. Additionally, Vitamin D levels tend to be lower when body fat is up, which may explain why obesity is associated with a poor prognosis for those with COVID-19.
Even though the body makes Vitamin D, our experience is that most patients who have their Vitamin D levels checked learn that they are deficient. Also, what is considered by most clinical labs to be the lower limits of normal may actually be too low for optimal protection. Therefore, most of us need to supplement.
What the evidence suggests8:
- Vitamin D reduces viral survival and replication.
- Vitamin D may decrease inflammation of the body’s hyperimmune response to the so-called ‘Cytokine Storm’, which is associated with the most severe COVID-19 infections. This proinflammatory tsunami is believed to cause severe damage to the lungs and other vital organs when it does occur.
- Vitamin D seems to increase the enzyme ACE-2, which is believed to protect against COVID-19. This ACE-2 decreases with age and in chronic illnesses such as diabetes and hypertension. ACE-2 is generally high in children which may be the reason why most kids are protected from severe COVID-19 infections.
Zinc
Zinc inhibits viral replication within the cells of our body. Many believe that the greater the viral load, the more overwhelming it is for your body to overcome the infection. Thus, by killing or inhibiting the reproduction of viruses such as COVID-19, Zinc allows our body’s natural immune defenses to neutralize the remaining viruses.
Quercetin
Quercetin is a plant bioflavonoid antioxidant that is believed to assist with the absorption of Zinc into our cells so as to maximize Zinc’s antiviral effects.
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Vitamin C is also believed to boost the overall immune system. Reduced Vitamin C levels are associated with poor health outcomes. Vitamin C is believed to increase Quercetin’s absorption and therefore leading to greater bioavailability of Zinc and its potential antiviral actions. Vitamin C helps facilitate the production and function of white blood cells, helping the body to defend against infections. Like Quercetin, Vitamin C is also an antioxidant, helping the body defend itself against the toxic effects of free radicals that are increased in infections.
Melatonin
Melatonin is believed to be an immune modulator possessing both anti-inflammatory or pro-inflammatory properties, depending on the body’s needs. Therefore, melatonin may prove to be of benefit with immune imbalance associated with the ‘Cytokine Storm’ associated with COVID-19, seen in the most severe cases. Melatonin has also been shown to have antiviral, antibacterial and antiparasitic properties. Melatonin is also believed to help regulate sleep.9
PROTECT THYSELF
Since the best defense against getting COVID-19 or the coronavirus is prevention, being vigilant and limiting contacts and exposure definitely will reduce the likelihood of infection and hence the complications. That being said, we can’t live in isolation indefinitely. Wearing a good quality mask when out in public has been shown to be protective. Initially it was thought that wearing a mask only protects the other guy but there is now good evidence that wearing a mask may decrease the severity of an acquired infection by the person wearing the mask along with its complications.
Protect Thyself and by doing so you will protect those around you!
* Statements made are for educational purposes and have not been evaluated by the US Food and Drug Administration. They are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. You should consult your healthcare practitioner before making decisions about health conditions and/or therapies.
CardioMender, MD has put together a package of Dr. Schiff’s personal choices for optimizing maintenance of the body’s immune defenses. Click this link or the picture for the CMMD Immune Defense Support Package.

References:
- Vitamin D deficiency as risk factor for severe COVID-19: a convergence of two pandemics https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.05.01.20079376v2.abstract D De Smet, K De Smet, P Herroelen, S Gryspeerdt… – MedRxiv, 2020 – medrxiv.org
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.05.01.20079376v2 - Merzon, E., et al., Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D3 level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study. MedRxiv, 2020.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/medrxiv/early/2020/07/03/2020.07.01.20144329.full.pdf - Panagiotou G, Tee SA, Ihsan Y, Athar W, Marchitelli G, Kelly D, Boot CS, Stock N, Macfarlane J, Martineau AR, Burns G, Quinton R. Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32621392/
- Accepted Date : 20-Jul-2020 Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study Eugene Merzon1,2*, Dmitry Tworowski3, Alessandro Gorohovski3, Shlomo Vinker1,2, Avivit Golan Cohen1,2, Ilan Green1,2, Milana Frenkel Morgenstern3* 1 Leumit Health Services, Tel-Aviv, Israel; 2 Department of Family Medicine, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel; 3 Cancer Genomics and BioComputing of Complex Diseases Lab, Azrieli Faculty of Medicine, Bar-Ilan University, Israel. as doi: 10.1111/FEBS.15495 This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved
- Martineau, A.R., Jolliffe, D.A., Hooper, R.L., Greenberg, L., Aloia, J.F., Bergman, P., DubnovRaz, G., Esposito, S., Ganmaa, D., Ginde, A.A. et al. (2017) Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. BMJ, 356, i6583. 44. Martineau, A.R., Jolliffe, D.A., Greenberg, L., Aloia, J.F., Bergman, P.,
- Dubnov-Raz, G., Esposito, S., Ganmaa, D., Ginde, A.A., Goodall, E.C. et al. (2019) Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: individual participant data meta-analysis. Health Technol Assess, 23, 1-44.
- Nutr Res. 2011 Jan;31(1):48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2010.12.001. Prevalence and correlates of vitamin D deficiency in US adults Kimberly Y Z Forrest 1, Wendy L Stuhldreher
- William Grant Med-Vu., www.vumedi.com/video/can-vitamin-d-reduce-the-risks-of-covid-19-infection-how-does-it-correlate-to-the-severity-of-illness
- Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Apr; 14(4): 8638–8683, Published online 2013 Apr 22.doi: 10.3390/ijms14048638 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3645767/